PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Verbalizes general impression of the patient 1 Determines responsiveness/level of consciousness 1 Determines chief complaint/apparent life threats 1 Assesses airway and breathing Assessment (1 point) Assures adequate ventilation (1 point) Initiates appropriate oxygen therapy (1 point) 3 Assesses circulationAug 08, 18 · standardized assessments to improve diagnosticaccuracy in adults and children with prolonged DoC (Level B) Clinicians should counsel families that for adults, MCS (vs vegetative state VS/ tant to educate families about patients' level of consciousness and function, inform prognostic counseling, and guide treatmentdecisionsNeurological assessment wwwwestafricaneducatednursesorg Feb 6, 16 pg 8 Levels of Consciousness Table 2 Levels of Consciousness Full consciousness The patient is alert, attentive, follows commands, responds promptly to external stimulation if asleep, and once awake, remains attentive
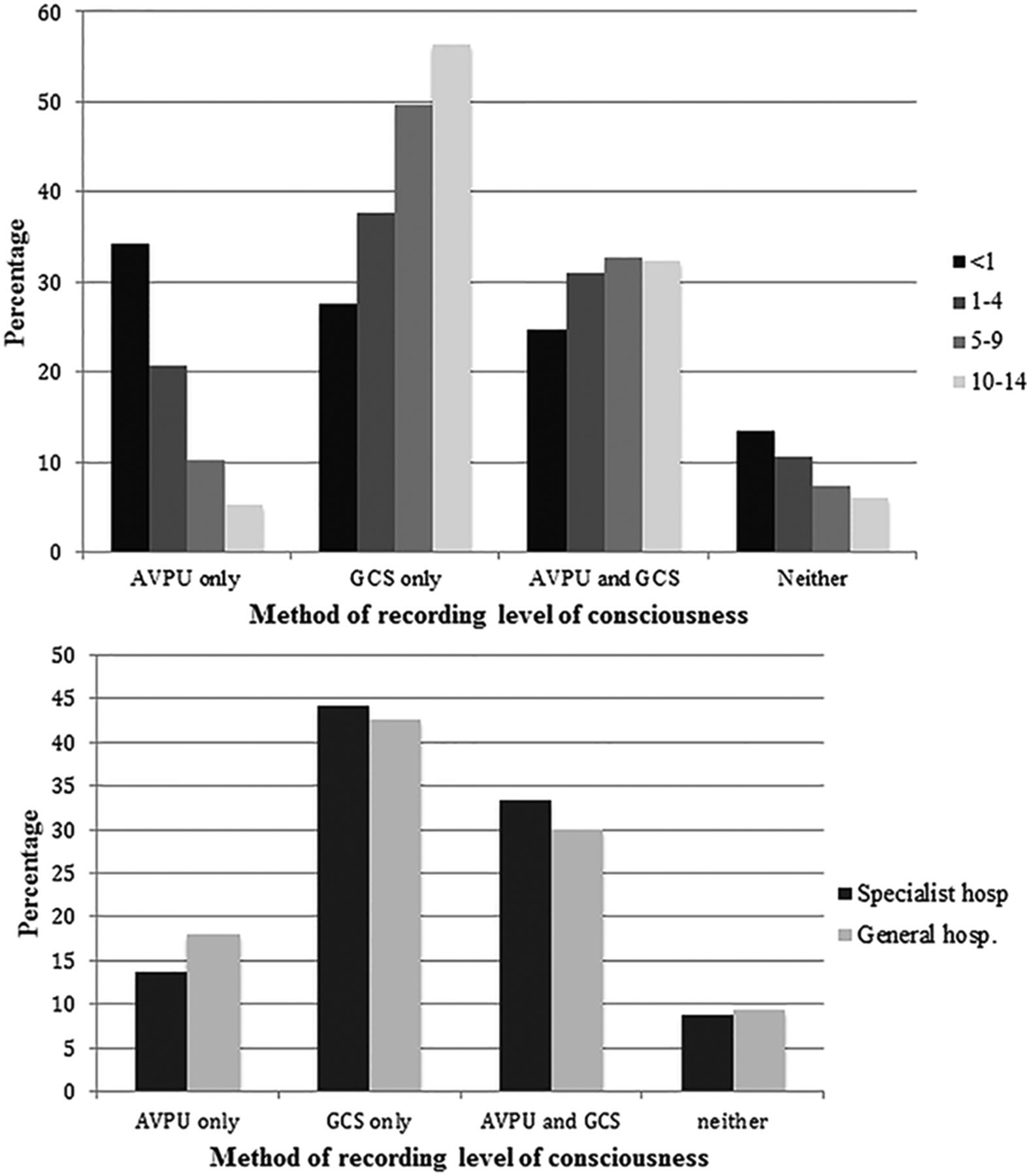
To What Extent Are Gcs And Avpu Equivalent To Each Other When Assessing The Level Of Consciousness Of Children With Head Injury A Cross Sectional Study Of Uk Hospital Admissions Bmj Open
Level of consciousness assessment pdf
Level of consciousness assessment pdf-An altered level of consciousness is any measure of arousal other than normal Level of consciousness (LOC) is a measurement of a person's arousability and responsiveness to stimuli from the environment A mildly depressed level of consciousness or alertness may be classed as lethargy;•Full Consciousness Alert, awake, responds appropriately to stimuli, follows commands •Confusion Disoriented, short attention span, agitated, restless, may have hallucinations •Lethargic Drowsy, delayed response to stimuli, slow in speech and mental process, & may drift off to sleep during exam Level of Consciousness 9



Pain Assessment Review Of Current Tools
Registered users can save articles, searches, and manage email alerts All registration fields are requiredThe assessment of level of cognition in patients with altered states of consciousness such as vegetative state and minimally conscious state is primarily based on the observation of spontaneous behaviours and those that occur in response to verbal, visual or tactile stimulationAssessment *An Assessment designation is intended for children coming into the care and custody of DFCS/DJJ for the first time Utilized when a child's current needs cannot be identified specifically enough to designate an appropriate level of services within the Levels of Care This usually occurs when there is a lack of
Richer & Tell, 03) For the first four months, patient level of consciousness was assessed using coma or low functioning assessment scales, and for the ensuing year and a half, Addenbrooke's Cognitive ASSESSING LEVEL OF CONSCIOUSNESS IN VS 309Jun 28, 08 · Each of the five examples includes an assessment of the central nervous system or level of consciousness, although the methods used are not identical 37 These scores have yet to be scientifically validated;Pain because of disorders of consciousness Hence, observational pain assessment instruments are warranted for these patientsAim The aim of this study was to study interrater agreement and sensitivity to change over time of an assessment scale developed for the evaluation of pain in severely braininjured patients with disorders of consciousness
8184 Teasdale G, Jennett B Assessment and prognosis of coma after head injury Acta Neurochir 1976;Apr 07, 16 · Assessment of consciousness 1 Assessment of consciousness Marwa Elhady lecturer of pediatrics Alazhar University 16 2 STIMULUS RESPONSE Assessment of level of consciousness start softly and then more loudly Level of consciousness is the most sensitive indicator of changes in the neurological state of the patient 3Assessment tool The Chart has been developed to reduce the amount of variation in chart design and to improve consistency in assessment skills and interpretation of assessment findings The Chart complies with the Between the Flags program indicates the level of consciousness



Assessment Of Consciousness In The Icu
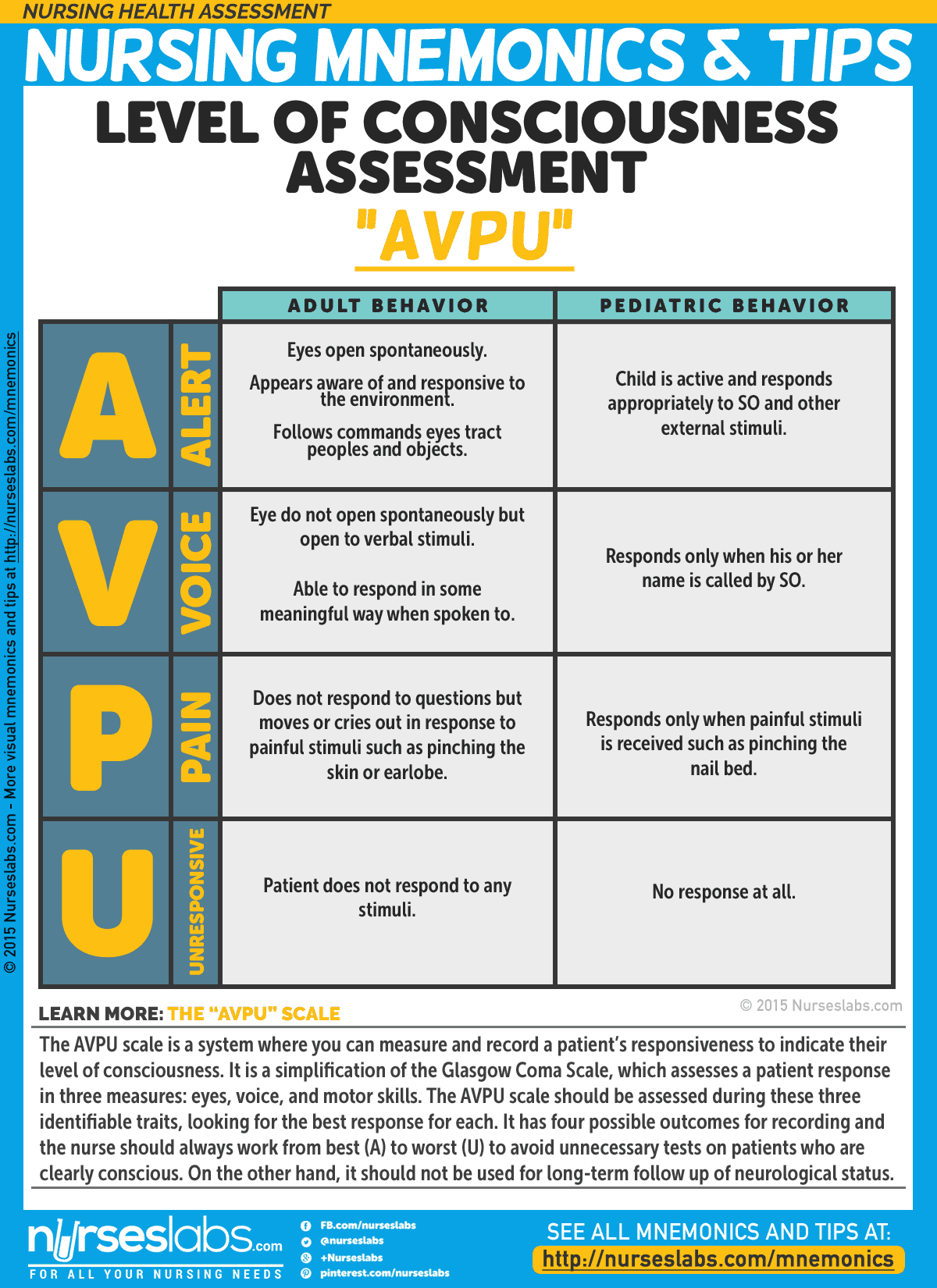


Nursing Health Assessment Mnemonics Tips Nurseslabs
The GCS should beSep 27, 19 · Assessment of disorders of consciousness Standardized assessments should be used for serial assessment eg, Coma Recovery Scale– Revised (CRSR), looks at auditory, visual, motor, orometer/verbal, communication, arousal Signs of emerging consciousness Visual tracking, nonstereotypic motor responses, emotional responses Spaulding RehabilitationJan 19, 12 · So, as an example of a two person test Statement "On a scale of 1 to 1,000 with 1 being the lowest level of truth and consciousness and 1,000 being the highest level of truth and consciousness, this article measures at level 0 (Y/N);


Unconscious Clients Patients Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Procedure



Moderate Sedation Assessment Test Welcome To The St Pages 1 4 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5
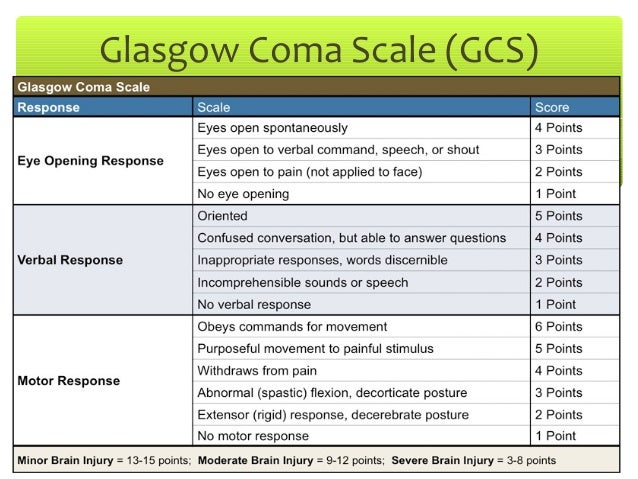
The Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) is a clinical scale used to reliably measure a person's level of consciousness after a brain injury The GCS assesses a person based on their ability to perform eye movements, speak, and move their body These three behaviors make up the three elements of the scale eye, verbal, and motorAssessment of Level of Consciousness A Stimulate with progressively stronger stimuli i) normal voice ii) shout iii) light touch iv) pain Observe patient's response (verbal or motor) If there is no response to voice or light touch, painful stimulus is needed to assess neurological status Central pain should be used firstSimple bedside assessment of level of consciousness comparison of two simple assessment scales with the Glasgow Coma scale* A F McNarry1 and D R Goldhill2 1 Research Registrar, 2 Senior Lecturer and Honorary Consultant in Anaesthesia and Critical Care Medicine, Department
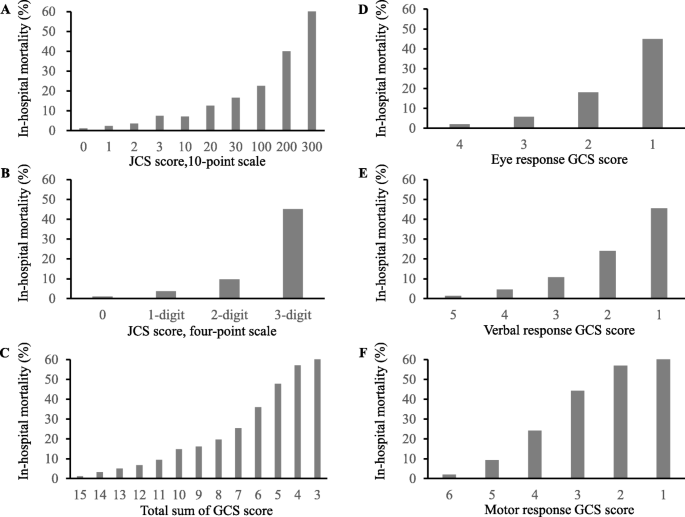


Association Of Japan Coma Scale Score On Hospital Arrival With In Hospital Mortality Among Trauma Patients Bmc Emergency Medicine Full Text
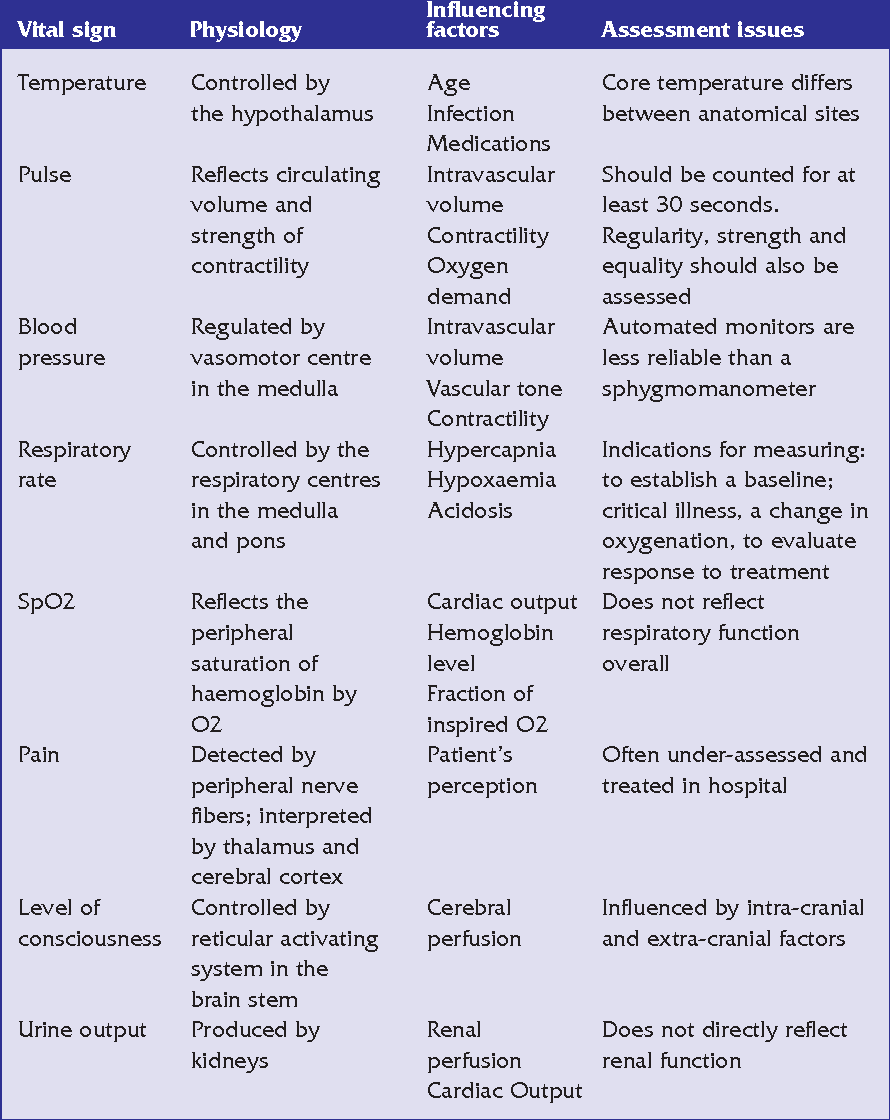


Pdf Critical Care The Eight Vital Signs Of Patient Monitoring Semantic Scholar
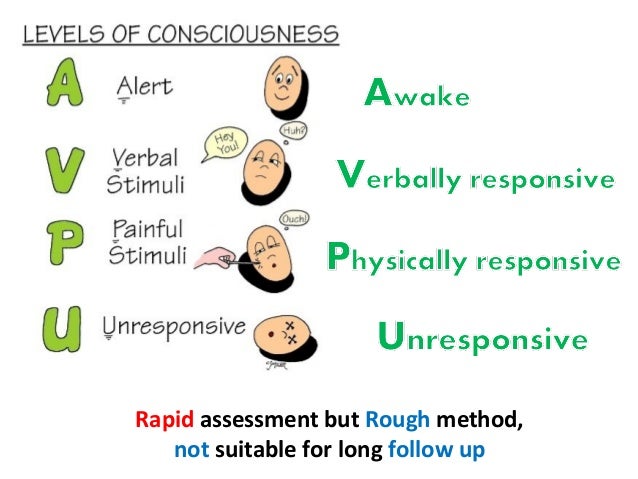
Altered Levels of Consciousness – Assessing Your Patient As health care professionals, sometimes the hardest thing at a stressful scene is figuring out why a patient has an altered mental status We want to quickly treat the patient but may have limitedTwo really important parts of neurological assessment are level of consciousness and mental status In fact, level of consciousness is THE most basic and sensitive indicator of altered brain function If we have a patient who is awake and alert for the 0700 assessment, but becomes lethargic or somnolent as the day progresses, this tells us thatJul 08, 08 · Level of consciousness It is not possible to directly assess the level of consciousness it can only be assessed by observing the patient's behavioural response to different stimuli During the initial rapid assessment of the critically ill patient, it is helpful to use the AVPU scale, with an examination of the pupils;
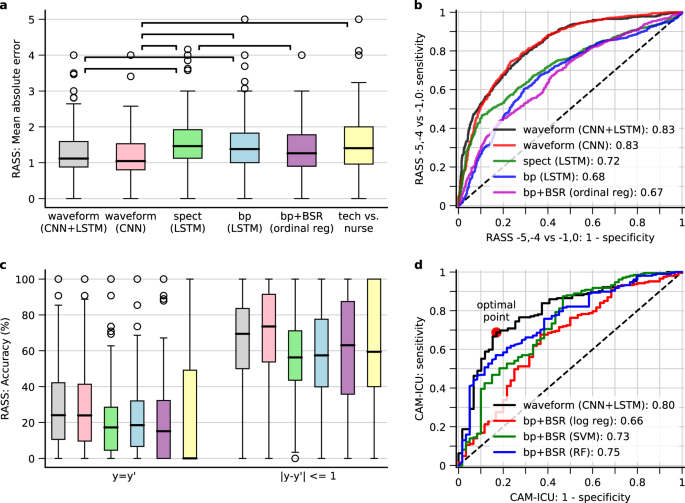


Automated Tracking Of Level Of Consciousness And Delirium In Critical Illness Using Deep Learning Npj Digital Medicine



Ultrasonic Thalamic Stimulation In Chronic Disorders Of Consciousness Brain Stimulation Basic Translational And Clinical Research In Neuromodulation
The psychological symptoms include mutism, stupor, or fluctuating levels of consciousness Hyperpyrexia develops with evidence of autonomic instability in the form of rapidly changing blood pressure, tachycardia, excessive sweating and urinary incontinence Plasma levels of the enzyme, creatinine phosphokinase, are increased to very high levelsNeurological Altered Level of Consciousness (LOC) Level of responsiveness and consciousness is the most important indicator of the patient's condition LOC is a continuum from normal alertness and full cognition (consciousness) to coma Altered LOC is not the disorder but the result of a pathology Coma Unconsciousness, unarousable unresponsivenessThe GCS was developed by Teasdale and Jennet in 1974 (2), aimed at standardizing assessment of level of consciousness in head trauma victims (3) The maximum score a patient can get in GCS is 15 Based on this scale, reduced consciousness has been classified into mild (GCS 1315), moderate (GCS 912) and severe (GCS 38) levels (4)



Using The Abcde Approach For All Critically Unwell Patients British Journal Of Healthcare Assistants



What Is The Nih Stroke Scale Nihss Score Saebo
Assessment of the unwell child FOCUS Reprinted from AustRAliAn FAmily PhysiciAn Vol 39, no 5, mAy 10 273 With knowledge of the child's appearance from the PAT and AVPU scale, if the disability assessment demonstrates altered level of consciousness, begin with general life support/monitoring with oxygen, cardiac monitoring, and pulse oximetryThe paper presents a proposal for incorporating the levels of consciousness into the framework of the integrative levels theory Keywords Integrative Levels, Consciousness, Levels of Consciousness, Animal Consciousness 1 Introduction Whether animals are conscious is an important issue in science and philosophy a present day intellectual chalMEDIC___7pdf You are called to the scene of a 3 yo patient that is demonstrating DIB and decreased level of consciousness Initial assessment reveals cyanosis of the lips The child is lethargic and cannot keep his eyes open Apply what you've learned Let's walk through


Abcde Approach To Emergency Management Simulation Geeky Medics



Head To Toe Assessment Template Pdf It Ru Ntnonto Reerreeri Rkt Head To Toe Assessment U2190 Level Of Consciousness Y O O O Awake Alert Restless O Course Hero
¾Review Neurological Assessment ¾Discuss the basic neuroanatomy and physiology ¾Describe the pathophysiology, management and nursing interventions of ¾Hydrocephalus ¾Cerebrovasculardisease ¾Meningitis ¾Seizures/status epilepticus ¾Head/Spinal Cord Injury ¾Neuromuscular Disorders Basic Neurologic Exam •Level of consciousnessOnce the level of consciousness is determined, a careful check for hints as to the cause of the alteration in level of consciousness should be undertaken In most instances the history (which can be obtained from the patient or those who accompany him, or from available medical records) is more valuable than is the examinationLevel of Consciousness The investigator must choose a response if a full evaluation is prevented by such obstacles as an endotracheal tube, language barrier, orotracheal trauma/bandages A 3 is scored only if the patient makes no movement (other than reflexive posturing) in response to noxious stimulation Scale Definition Level of



Pain Assessment Review Of Current Tools



Assessing The Conscious Level In Infants And Young Children A Paediatric Version Of The Glasgow Coma Scale Semantic Scholar
Assessment (Smith, 03) NICE (07) recommends using GCS to assess all patients with head injuries Before assessment, ascertain the patient's acuity of hearing, medical history and any indications that may affect level of consciousness AVPU The AVPU scale is a quick and easy method to assess level of consciousness It is idealAims and objectives To study practice in consciousness assessment among neuroscience nurses in Europe Background Over the years, several instruments have been developed to assess the level of consciousness for patients with brain injury It is unclear which instrument is being used by nurses in Europe and how they are trained to use these tools adequatelySep 01, 01 · Assessment of coma Coma is an acute, life threatening situation Evaluation must be swift, comprehensive, and undertaken while urgent steps are taken to minimise further neurological damage3 Emergency management should include resuscitation with support of cardiovascular and respiratory system;
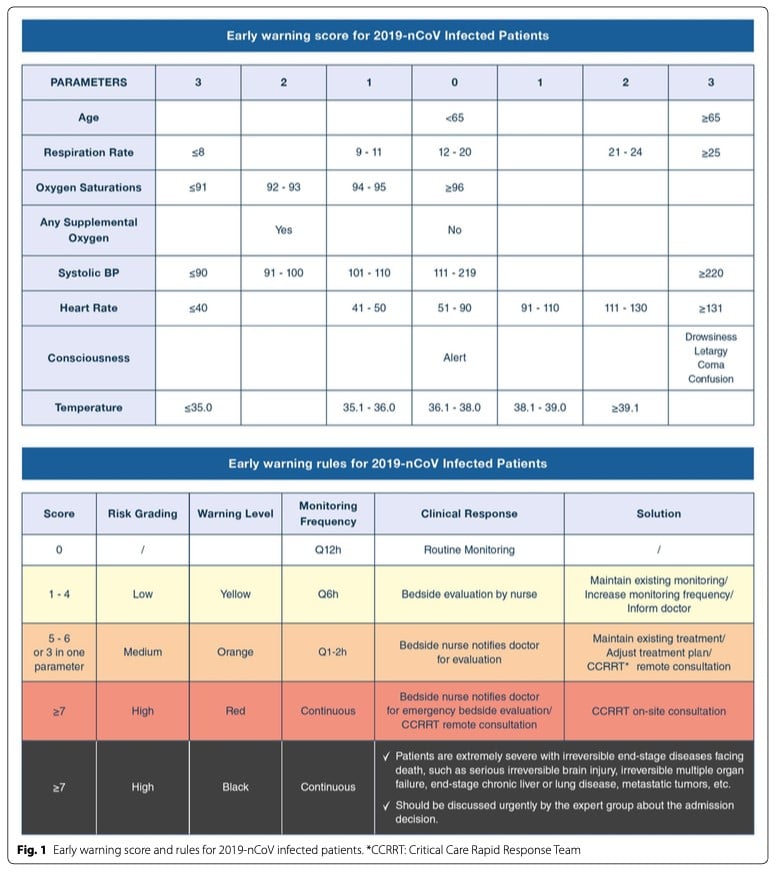


News Or News2 Score When Assessing Possible Covid 19 Patients In Primary Care The Centre For Evidence Based Medicine



Nih Stroke Scale Nihss Modified Nihss Mnihss Peripheral Brain Nih Stroke Scale Emergency Nursing Mcat Motivation
Medical Control Guideline LEVEL OF CONSCIOUSNESS PRINCIPLE 1 Evaluation and documentation of the patient's level of consciousness are key components of a thorough patient assessment 2 The patient's baseline level of consciousness should be taken into consideration when evaluating whether the altered level of consciousness (ALOC) findingCategorization Coma No eye opening, no ability to follow commands, no word verbalizations (38) Head Injury ClassificationEach stage of consciousness is identified with a color, for easy reference4 It is important to recognize that these "stages" are not strict levels, like rungs on a ladder They are more like loosely delineated areas along a spectrum of development Thus, a stage is more like a probability wave than a concrete level of consciousness



Glasgow Coma Scale Gcs How To Assess Gcs Geeky Medics



Cia Document The Gateway Experience Nature Of Consciousness Reality Pdf Included Update 18 2 21 Youtube
Scale, comprised of 4 grades of consciousness, is the simplest and the fastest method for assessment of neurologic status (1,11) Nonetheless, its value has been limited by the broad range of definitions for each grade This prompted us to assessment of consciousness levelAssessment Evaluation of level of consciousness (LOC) and mentation are the most important parts of the neuro exam A change in either is usually the first clue to a deteriorating condition The following terms are commonly used to describe a decreased LOC, so itHowever, we have shown the importance of neurological assessment in identifying patients who might require escalation to a critical



Neurological Assessment 1 Assessing Level Of Consciousness Nursing Times



Pdf Awakening Biodiversity Consciousness Tamasin Ramsay Academia Edu
Level of consciousness (GCSACUTE ASSESSMENT SCALES GLASGOW COMA SCALE (GCS) • Identifies ocular, verbal, and motor response to examination • Tool is used to communicate the level of consciousness (LOC) of patients with an acute brain injury • The scale was developed to complement and not replace assessments of other neurological functions • Strength Fast andCheck a blood glucose level • Look for incontinence • Check the patient's temperature – fever can often be found with infectious disorders as well as after prolonged seizure related hypoor change in level of consciousness • Do a full headtotoe assessment to look for signs of traumaand/or drug use (eg track marks) MANAGEMENT


Coma Scales A Historical Review



Pdf Comparison Of Three Consciousness Assessment Scales In Poisoned Patients And Recommendation Of A New Scale Avpu Plus
May 01, 1984 · An alternative method of coma assessment is presented and compared with the Glasgow Coma Scale The merits of the Comprehensive Level of Consciousness Scale as a research tool are presented An analysis of 101 consecutive consciousnessimpaired patients with their shortterm outcome is presentedTeasdale G, Jennett B Assessment of coma and impaired consciousness Lancet 1974;At 400 (Y/N) and so on, and can even be refined right down to the exact number if that is



Pdf Assessing Level Of Consciousness And Cognitive Changes From Vegetative State To Full Recovery


Evolve The Organization By Measuring And Developing Its Consciousness Management Innovation Exchange
Mar 27, 18 · Assess Level of Consciousness An individual's level of consciousness can deteriorate due to many different reasons, such as head injuries, increased intracranial pressure, haemorrhage, or lesions and tumours Determining the level of consciousness depends on the individual you are assessing and can be easy or difficultTeristics (educational level, years of experience, level of specialisation and work setting) and five for evaluation of the questionnaire The remaining questions (Supporting Information Appendix S1) were related to consciousness assessment where conditional logic ensured that participants would only receive the questions that would apply toLevel The RanchoPediatric can be used in any setting, whether the child is at a hospital, a rehabilitation center, home, or school Knowing the child's Level of Consciousness (LOC) is the key to understanding the child's cognitive and behavioral skills and may help to determine what further assessment, intervention, and education plans may



Free 7 Sample Nursing Assessment Forms In Pdf Ms Word


Identification And Evaluation Of Observational Measures For The Assessment And Or Monitoring Of Level Of Consciousness In Adult Palliative Care Patients A Systematic Review For I Can Care Ucl Discovery
Clinical assessment tools –The Law Mental Capacity Act 05 –Disorders of consciousness persisting > 4 weeks After severe sudden onset brain injury PDOC also occur as a final stage of neurodegenerative disease – may be responsive, albiet at reflexive levelCorrection of immediate metabolic upset, notably controlTo ensure consistent management of patients with an altered level of consciousness Scope Applies to Queensland Ambulance Service (QAS) clinical staff Risk assessment • Nil in this setting Altered level of consciousness February, 21 _DCPM_pdf


Coma Scales A Historical Review



Pediatric Patient Assessment Assessment Triangle Pages 1 12 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5
Someone in this state can be aroused with little difficulty People who are obtunded



Neurological Assessment Ed Areyouprepared



Taking Your Ipad To The Max Ios 5 Edition 11



1 Neurological Assessment At The End Of This Self Study The Participant Will 1 Describe The Neuro Nursing Assessment 2 List 5 Abnormal Findings In A Neuro Ppt Download



Pdf The Glasgow Coma Scale And Other Neurological Observations



Glasgow Coma Scale



Pdf Assessment Scales For Disorders Of Consciousness Evidence Based Recommendations For Clinical Practice And Research



Neurological Associations Of Covid 19 The Lancet Neurology
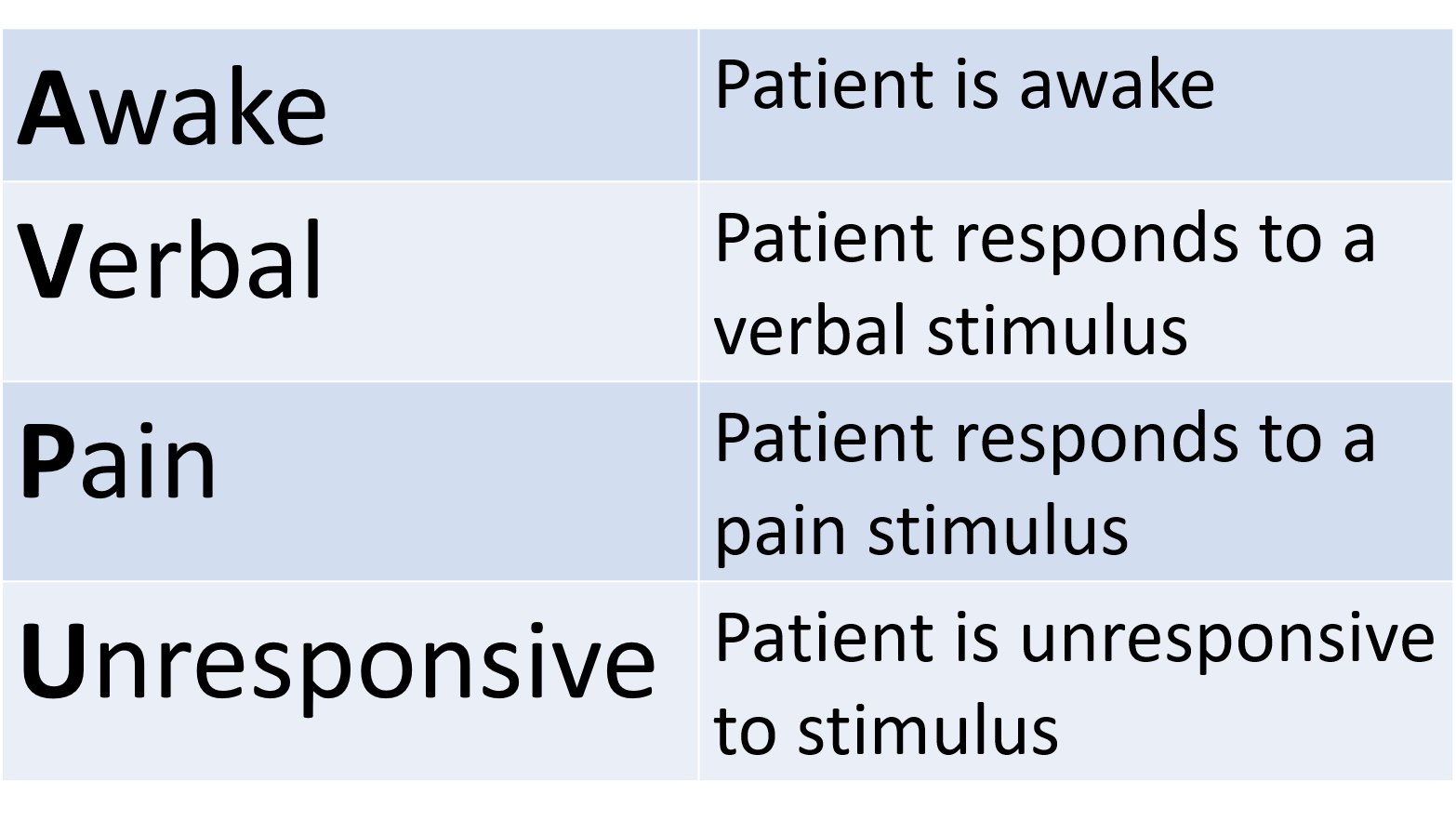


How To Use Avpu To Check Level Of Consciousness



Assessment For Levels Of Consciousness Acvpu And The Glasgow Coma Scale



Medscape Log In Nih Stroke Scale Icu Nursing Nurse Brain Sheet



Pdf Identification And Evaluation Of Observational Measures For The Assessment And Or Monitoring Of Level Of Consciousness In Adult Palliative Care Patients A Systematic Review For I Can Care



Pdf The Glasgow Coma Scale In Adults Doing It Right
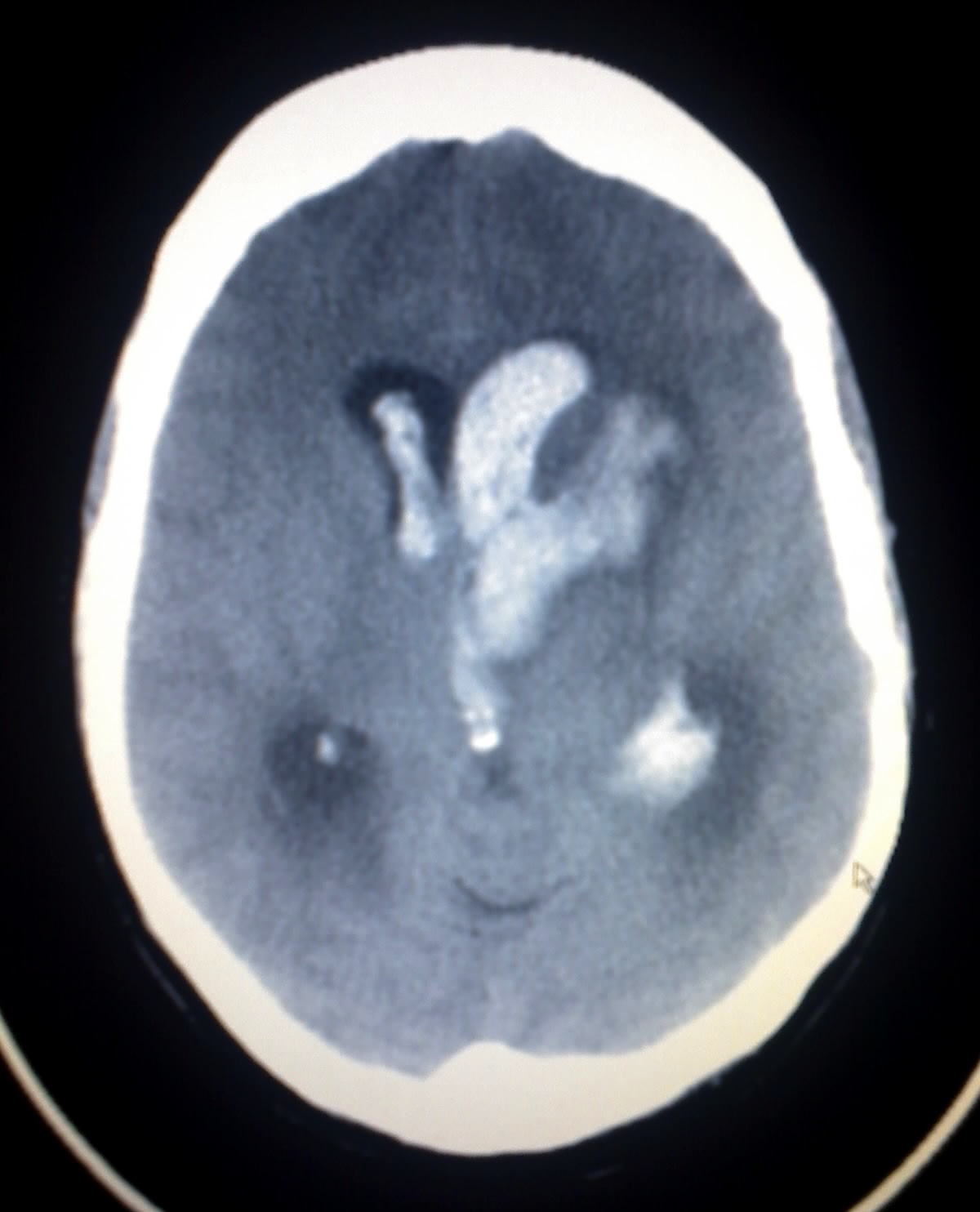


Altered Level Of Consciousness Wikipedia



The Neurology Of Consciousness 2nd Edition



Patient Assessment Event Medicine Group Education Planning Operations



To What Extent Are Gcs And Avpu Equivalent To Each Other When Assessing The Level Of Consciousness Of Children With Head Injury A Cross Sectional Study Of Uk Hospital Admissions Bmj Open



Amp Pinterest In Action Nursing Assessment Neurological Assessment Nursing Physical Assessment



Patient Assessment Event Medicine Group Education Planning Operations



Pdf Assessment Scales For Disorders Of Consciousness Evidence Based Recommendations For Clinical Practice And Research
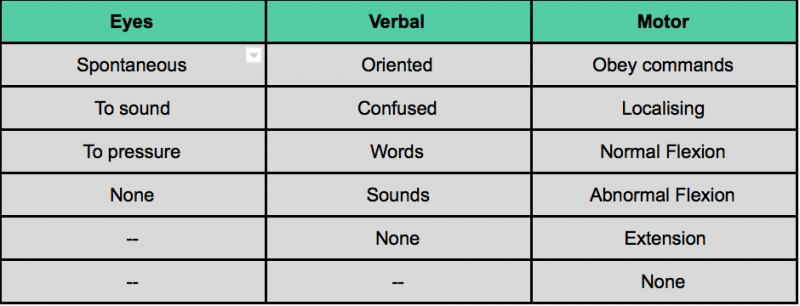


Glasgow Coma Scale Physiopedia
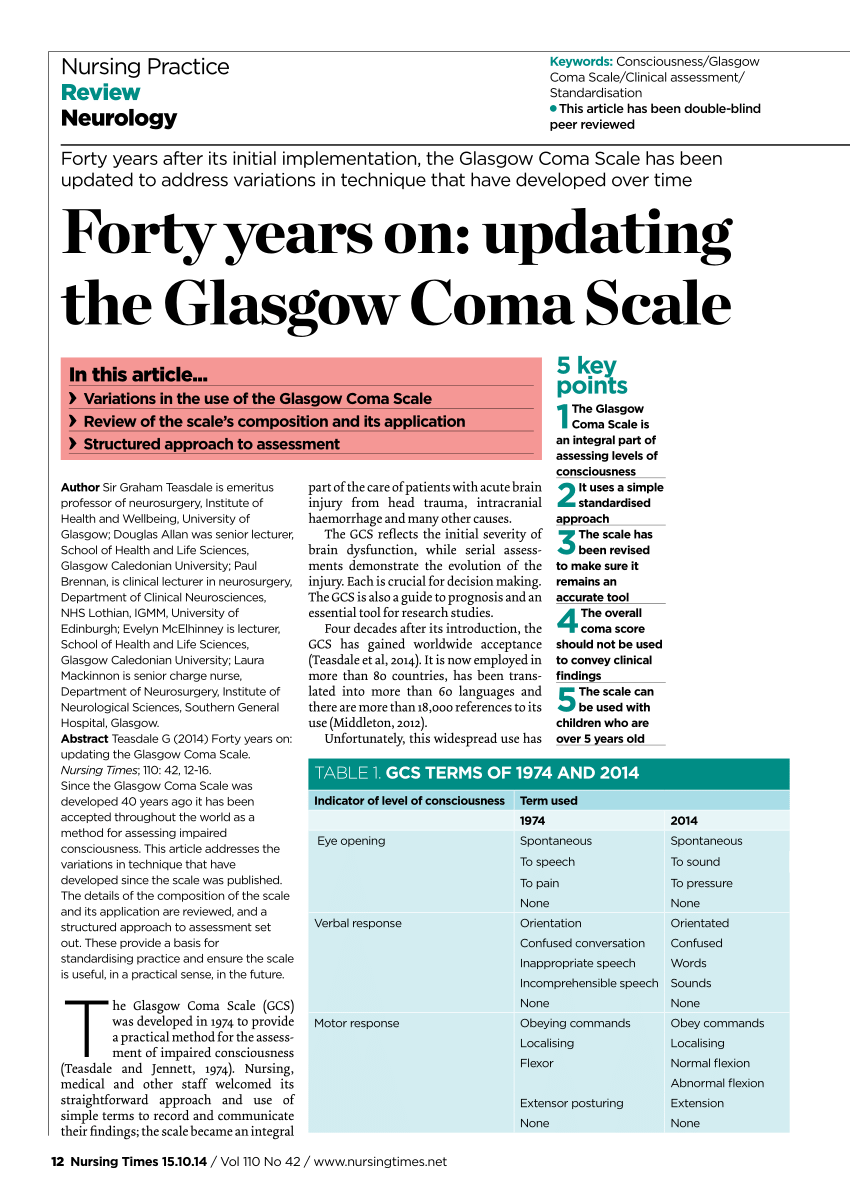


Pdf Forty Years On Updating The Glasgow Coma Scale



Ems Assessment Notes Pdf Available For Instant Download For Etsy
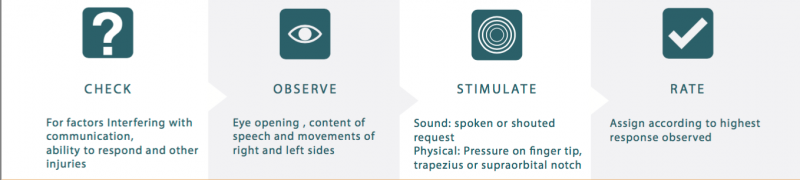


Glasgow Coma Scale Physiopedia


Assessment Of Consciousness



Glasgow Coma Scale Coma Diseases And Disorders


Social Phobia Scale Sps Novopsych



Caring For Neurosurgical Patients With External Ventricular Drains Nursing Times


Deep Structural Brain Lesions Associated With Consciousness Impairment Early After Hemorrhagic Stroke Scientific Reports



Beyond The Basics Trauma Assessment Ems World



Assessment For Levels Of Consciousness Acvpu And The Glasgow Coma Scale


Management Of Clients With Altered Level Of Consciousness
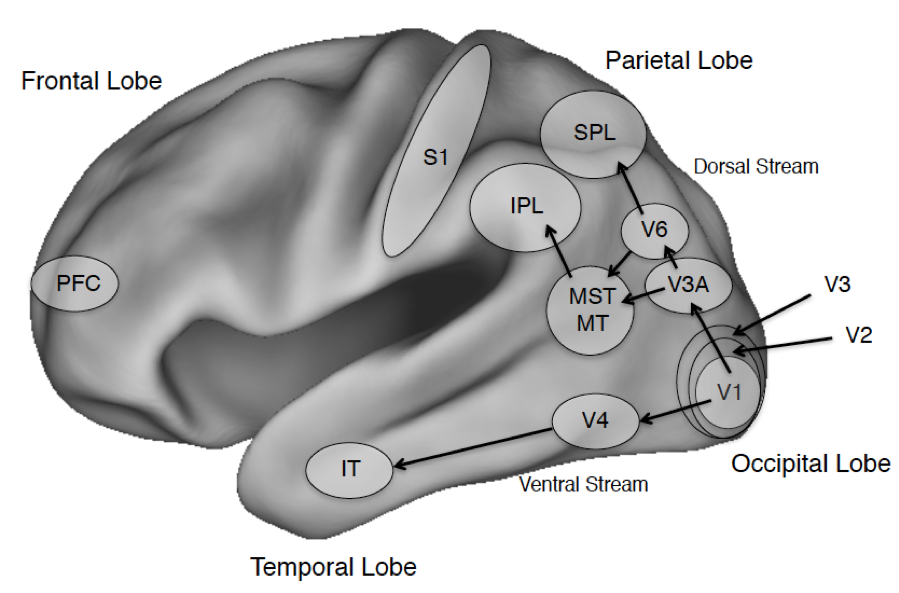


The Neuroscience Of Consciousness Stanford Encyclopedia Of Philosophy


Coma Scales A Historical Review



Levels Of Consciousness


Outcome Prediction Of Consciousness Disorders In The Acute Stage Based On A Complementary Motor Behavioural Tool



Scene Size Up Primary Assessment Emergency Care And Pages 1 5 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5



Ten Point Guide To Mental State Examination Mse In Psychiatry



Pdf The Theory Of Six Main Levels Of Consciousness A Study Of The Third Level Tina Lindhard Academia Edu



Top Pdf Sensory Stimulation Assessment Measure Ssam 1library



Nih Stroke Scale Printable Pdf Fill Online Printable Fillable Blank Pdffiller
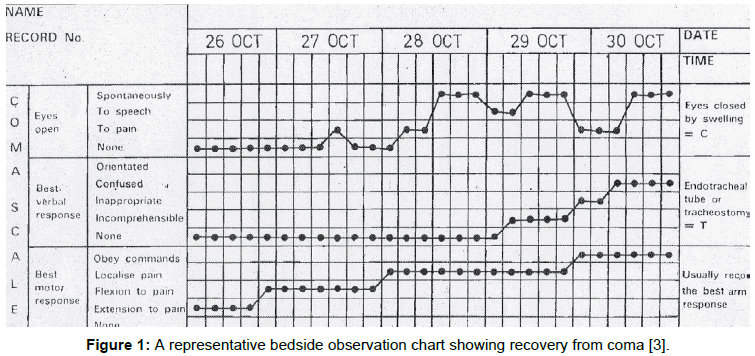


The Glasgow Coma Scale A Breakthrough In The Assessment Of The Level Of Consciousness



Pdf Assessment Scales For Disorders Of Consciousness Evidence Based Recommendations For Clinical Practice And Research



Assessment Of Level Of Consciousness With Coma Recovery Scale Among Patients With Traumatic Brain Injury Indian Journal Of Public Health Research Development


Effect Of Sensory Stimulation Assessment Measure Ssam On Level Of Consciousness Among Clients With Total Brain Injury Tbi At Selected Hospital Chennai Eprints Tamil Nadu Dr Mgr Medical University



Glasgow Coma Scale
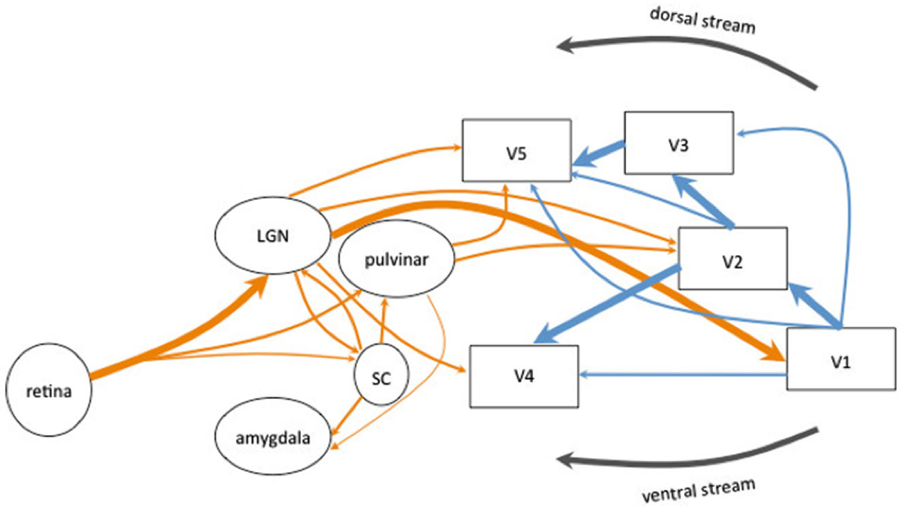


The Neuroscience Of Consciousness Stanford Encyclopedia Of Philosophy



aaa Cheat Sheet Pdf



Fuahydjvttzmem



European Academy Of Neurology Guideline On The Diagnosis Of Coma And Other Disorders Of Consciousness Kondziella European Journal Of Neurology Wiley Online Library



Braden Scale Pdf Fill Online Printable Fillable Blank Pdffiller
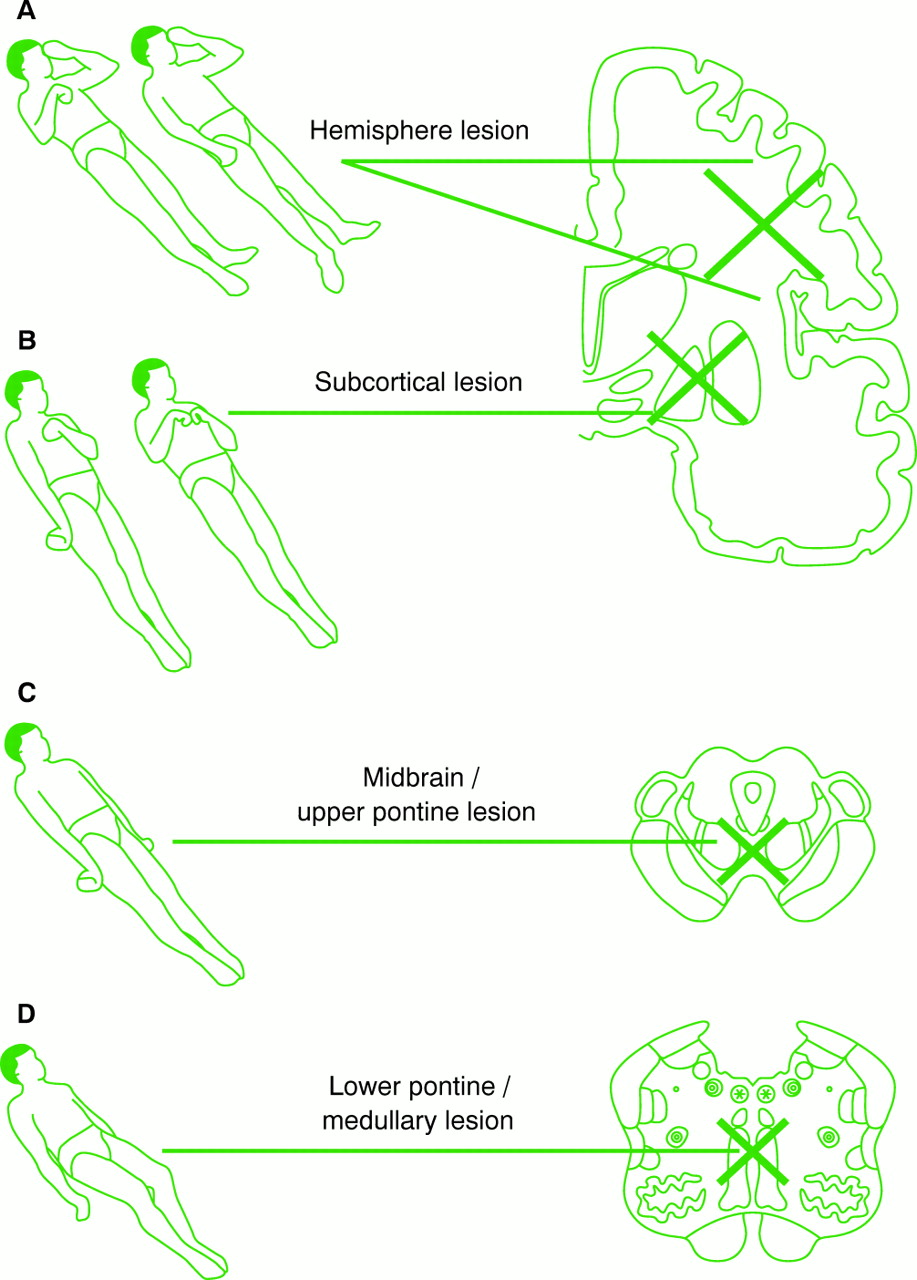


Neurological Assessment Of Coma Journal Of Neurology Neurosurgery Psychiatry



Pain Assessment Review Of Current Tools



European Academy Of Neurology Guideline On The Diagnosis Of Coma And Other Disorders Of Consciousness Kondziella European Journal Of Neurology Wiley Online Library



Management Of Clients With Altered Level Of Consciousness



Patient Assessment Event Medicine Group Education Planning Operations



Apply First Aid Drabcd Action Plan


Association Of Japan Coma Scale Score On Hospital Arrival With In Hospital Mortality Among Trauma Patients Bmc Emergency Medicine Full Text



Seven Levels Of Leadership Consciousness



Unconsciousness An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿